Modern methods of welding can be classified, depending on the state of the material during welding (plastic or molten state), as follows:
Plastic welding or pressure welding (explained below)
Fusion welding or nonpressure welding (explained below)
They can also be classified, depending on the source of heat, as follows:
1. Gas welding
Oxy acetylene or hydrogen welding (explained below)
Air acetylene welding
2. Arc welding (explained below)
Carbon arc welding
Metal arc welding
Gas metal arc welding (MIG)
Plasma arc welding
Electro slag welding (explained below)
Submerged arc welding
Flux cored arc welding
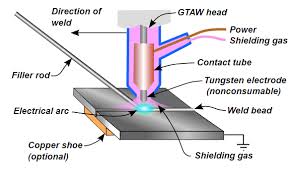
Gas tungsten arc welding (TIG)
Atomic hydrogen arc welding
3. Resistance welding (explained below)
Butt welding
Resistance butt welding
Spot welding
Seam welding
Projection welding
Percussion welding
4. Thermit welding (explained below)
5. Solid state welding
Friction welding (explained below)
Ultrasonic welding (explained below)
Diffusion welding (explained below)
Explosive welding (explained below)
Cold welding (explained below)
Forge welding
6. New welding processes
Electron beam welding (explained below)
Laser beam welding (explained below)
Related Processes
Arc weld
Hard pressing weld
Oxy acetylene cutting
Brazing
Soldering
Some of the most important welding processes are explained below:
Plastic welding or pressure welding:
In this process, the piece of metal to be joined is heated to a plastic state and then forced together by external pressure.
Fusion welding or nonpressure welding:
In this type of welding method, the material at the joint is heated to a molten state and allowed to solidify. This include gas weld, arc weld etc.





No comments:
Post a Comment